Allen Yi-Lun Tsai
Research highlight
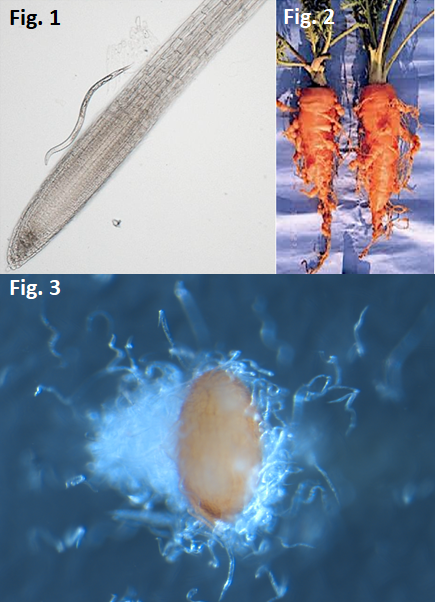
Nematodes are small worm-like animals found in many environments in the
world. Among them, root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita, Fig. 1) are economically important pathogens that affects many regions
of the world, including Kyushu, Japan. These nematodes are plant parasites
that infect roots to absorb nutrients from the plant hosts, causing serious
agricultural damages (Fig. 2).
It is believed that plant-pathogenic nematodes detect chemicals secreted
from plants to find hosts. We are interested in what plant-secreted chemicals
affect nematode behaviors, and how nematodes perceive and respond to these
chemicals. For example, we have found that nematodes are attracted to certain
compounds secreted from the seeds (Fig. 3). Through our research, we hope
to develop new strategies to protect crop plants from pathogens.
Résumé
2013.06: PhD, Department of Cells & Systems Biology, University of
Toronto
2013.01 - 2015.03: Post-doctoral researcher, Department of Botany, University
of British Columbia
2015.04 - 2019.03: Post-doctoral researcher, Graduate School of Science
and Technology, Kumamoto University
2019.04 - 2020.10: Special Post-Doctoral Researcher, Center for Sustainable
Resource Science, Riken
2020.10 - present: Assistant professor, Faculty of Advanced Science and
Technology, Kumamoto University
Contact information
Tel:
(+81) 096-342-3436
Email: tsai-yilun(at)kumamoto-u.ac.jp
Address:
2-39-1 Kurokami, Chuo-ku, Kumamoto, 860-8555 JAPAN
Kurokami South campus
Room C217, Faculty of Science Building 1
PhD., Assistant professor
Plant molecular biology
Department of Molecular Agriculture
Select publications
VND Genes Redundantly Regulate Cell Wall Thickening during Parasitic Nematode
Infection. Saki Gushino, Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Misato Otani, Taku Demura, Shinichiro Sawa. Plant And Cell Physiology,
2024/4/25
Root-knot nematode modulates plant CLE3-CLV1 signaling as a long-distance
signal for successful infection. Satoru Nakagami, Michitaka Notaguchi,
Tatsuhiko Kondo, Satoru Okamoto, Takanori Ida, Yoshikatsu Sato, Tetsuya
Higashiyama, Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Takashi Ishida, Shinichiro Sawa. Science Advances, 9(22), 2023/6/2
A mechanical theory of competition between plant root growth and soil pressure
reveals a potential mechanism of root penetration. Haruka Tomobe, Satoru
Tsugawa, Yuki Yoshida, Tetsuya Arita, Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Minoru Kubo, Taku Demura, Shinichiro Sawa. Scientific Reports, 13(1),
2023/5/9
Rhamnogalacturonan-I as a nematode chemoattractant from Lotus corniculatus
L. super-growing root culture. Morihiro Oota, Syuuto Toyoda, Toshihisa
Kotake, Naoki Wada, Masatsugu Hashiguchi, Ryo Akashi, Hayato Ishikawa,
Bruno Favery, Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Shinichiro Sawa. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 2023/1/26
Local auxin synthesis mediated by YUCCA4 induced during root-knot nematode
infection positively regulates gall growth and nematode development. Reira
Suzuki, Yuri Kanno, Patricia Abril-Urias, Mitsunori Seo, Carolina Escobar,
Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Shinichiro Sawa. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022/11/16
Asymmetric distribution of extracellular matrix proteins in seed coat epidermal
cells of Arabidopsis is determined by polar secretion. Yi‐Chen Lee, Gillian
H. Dean, Erin Gilchrist, Allen Yi‐Lun Tsai, George W. Haughn. Plant Direct, 5(11), 2021/11
PUCHI Regulates Giant Cell Morphology During Root-Knot Nematode Infection
in Arabidopsis thaliana. Reira Suzuki, Mizuki Yamada, Takumi Higaki, Mitsuhiro
Aida, Minoru Kubo, Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Shinichiro Sawa. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12 755610-755610, 2021/10/6
Root-knot nematode chemotaxis is positively regulated by l-galactose sidechains
of mucilage carbohydrate rhamnogalacturonan-I. Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Yuka Iwamoto, Yoichi Tsumuraya, Morihiro Oota, Teruko Konishi, Shinsaku
Ito, Toshihisa Kotake, Hayato Ishikawa, Shinichiro Sawa. Science advances,
7(27), 2021/7
Seed Mucilage: Biological Functions and Potential Applications in Biotechnology.
Allen Yi-Lun Tsai, Robert McGee, Gillian H Dean, George W Haughn, Shinichiro Sawa. Plant
& cell physiology, 2021/7/1